A Natural Electrical Phenomenon: Red And Green Lights In The Sky
You ever heard of the magical dance in the sky that paints the heavens with red and green hues? Well, buckle up because we’re diving deep into one of nature’s most breathtaking spectacles: red and green lights in the sky. These aren’t just random sparkles—they’re a natural electrical phenomenon that’s been fascinating scientists and stargazers alike for centuries. So, what exactly is this marvel, and why should you care? Let’s find out!
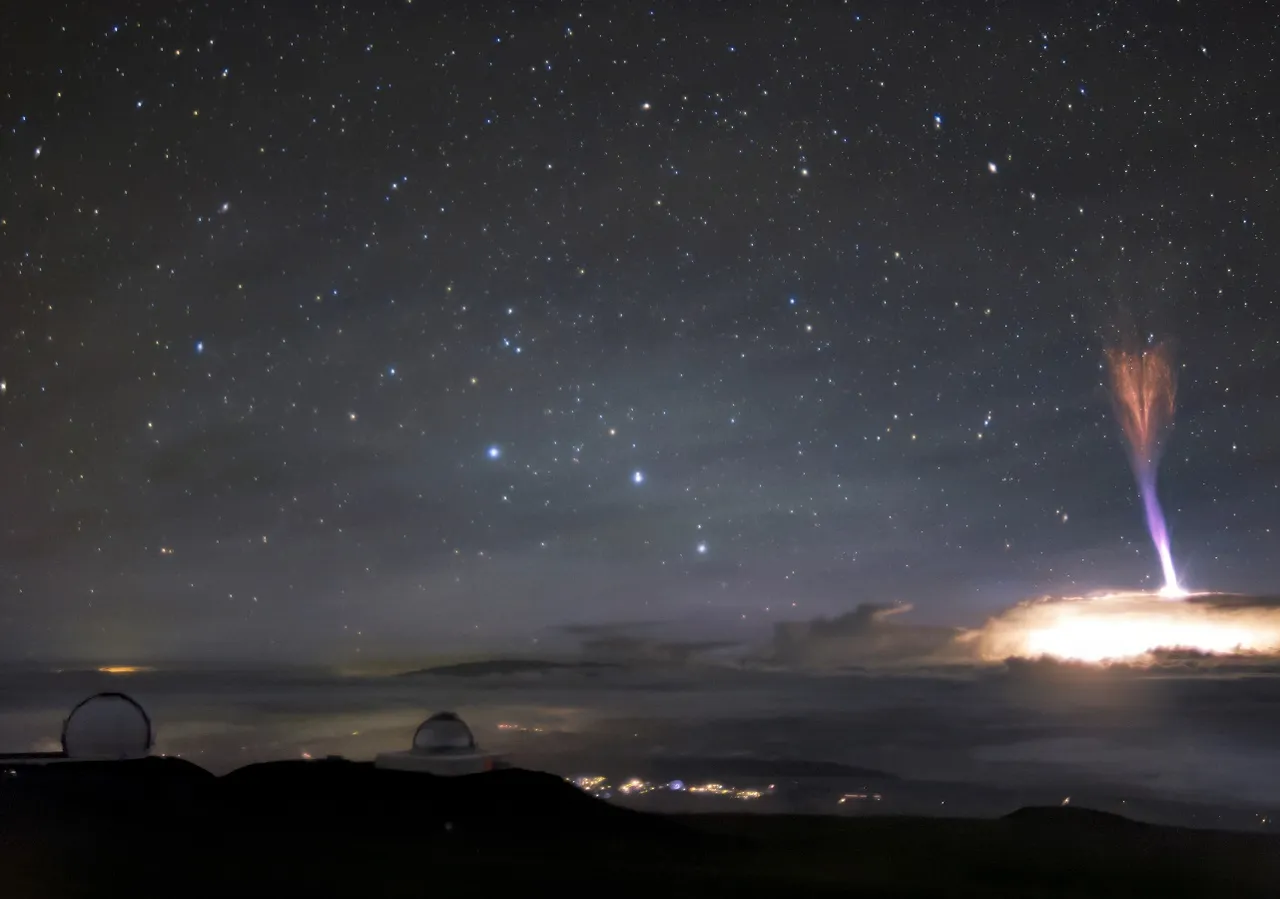
Imagine yourself standing under a pitch-black sky, far away from city lights. Suddenly, the horizon starts glowing with colors so vibrant, it feels like the universe is putting on a show just for you. That, my friend, is what we call auroras—specifically, the red and green lights that light up the polar regions. These lights aren’t just beautiful; they’re also a testament to the incredible forces at play in our atmosphere.
But here’s the kicker: understanding these phenomena isn’t just about marveling at their beauty. It’s about unraveling the mysteries of our planet’s interaction with the cosmos. Whether you’re a scientist, an adventurer, or just someone who loves staring at the stars, red and green lights in the sky are worth exploring. So grab your coat, head outside, and let’s decode this cosmic phenomenon together.
- Unlocking The Power Of Knowledgelink Uva A Comprehensive Guide To Transform Your Learning Journey
- Unveiling The Jaws Cast The Story Behind The Blockbusters Iconic Performances
What Are Red and Green Lights in the Sky?
Let’s break it down real quick. Red and green lights in the sky, often referred to as auroras, are essentially nature’s light show. They occur when charged particles from the sun, also known as solar wind, collide with Earth’s magnetic field. This collision triggers a reaction in the upper atmosphere, where these particles interact with gases like oxygen and nitrogen. The result? A dazzling display of colors that can range from vibrant green to deep red.
But why red and green, you ask? Well, it all depends on the altitude and the type of gas involved. Green auroras, which are the most common, occur around 60 to 150 miles above the Earth’s surface, where oxygen atoms emit their signature glow. Red auroras, on the other hand, happen at much higher altitudes, above 150 miles, where oxygen atoms take a little longer to release their energy. It’s like a cosmic game of ping-pong, but way cooler.
How Do Auroras Form?
Alright, let’s dive deeper into the science behind this spectacle. Auroras are born in the sun, where solar storms eject massive amounts of charged particles into space. These particles, also known as the solar wind, travel through the cosmos until they reach Earth’s magnetic field. When they do, they’re funneled towards the polar regions, where they collide with our atmosphere.
- Mastering Rope Pull Techniques Unlock Your Strength And Efficiency
- Boob Pedia The Ultimate Guide To Understanding And Appreciating The Female Form
Here’s where things get interesting. As these charged particles crash into oxygen and nitrogen atoms in the atmosphere, they transfer their energy, causing the atoms to become excited. This excitement doesn’t last long, though. Once the atoms calm down, they release the energy in the form of light—creating the mesmerizing colors we see in the sky. It’s like a cosmic light bulb, powered by the sun!
Factors Influencing Aurora Activity
Not all auroras are created equal. Several factors influence their intensity, color, and frequency. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Solar Activity: The more active the sun is, the more intense the auroras tend to be. Solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) can supercharge the solar wind, leading to more vibrant displays.
- Earth’s Magnetic Field: Our planet’s magnetic field plays a crucial role in shaping auroras. It acts like a shield, guiding the charged particles towards the poles.
- Atmospheric Conditions: Clear skies and minimal light pollution are essential for observing auroras. If the weather’s not cooperating, you might miss the show entirely.
Where Can You See Red and Green Lights in the Sky?
If you’re hoping to catch a glimpse of these celestial wonders, you’ll need to head to the polar regions. The most famous aurora hotspots include:
- Alaska, USA: Fairbanks is often hailed as one of the best places to witness the northern lights.
- northern Scandinavia: Countries like Norway, Sweden, and Finland offer breathtaking views of auroras, especially during winter months.
- Iceland: With its dramatic landscapes and minimal light pollution, Iceland is a dream destination for aurora hunters.
- Canada: The Yukon Territory and the Northwest Territories are prime locations for spotting auroras.
But here’s a fun fact: you don’t always have to travel to the poles. During intense solar storms, auroras can sometimes be seen as far south as the United States or even Europe. So keep an eye on space weather forecasts—you might get lucky!
Why Are Red and Green Lights in the Sky Important?
Beyond their aesthetic appeal, auroras serve as a valuable tool for scientists studying Earth’s magnetic field and the sun’s influence on our planet. By observing auroras, researchers can gain insights into:
- Space Weather: Understanding how solar activity affects our atmosphere is crucial for protecting satellites, communication systems, and even power grids.
- Climate Studies: Auroras can provide data on atmospheric composition and temperature, helping scientists model climate change.
- Geological Research: The interaction between Earth’s magnetic field and solar particles can reveal information about the planet’s core and geological history.
So the next time you see a red or green light in the sky, remember that it’s not just a pretty picture—it’s a window into the workings of our universe.
Historical Significance of Auroras
Humans have been fascinated by auroras for thousands of years. Ancient civilizations often viewed them as mystical or divine phenomena. For example:
- Native American Tribes: Some tribes believed auroras were the spirits of their ancestors dancing in the sky.
- Vikings: The Norsemen thought auroras were reflections of the armor worn by Valkyries, warrior maidens who chose which soldiers would die in battle.
- Chinese Mythology: In ancient China, auroras were sometimes interpreted as celestial dragons battling in the heavens.
Even today, auroras continue to inspire artists, writers, and filmmakers. They remind us of the beauty and mystery of the universe, sparking our curiosity and imagination.
How to Photograph Red and Green Lights in the Sky
Want to capture the magic of auroras on camera? Here are some tips to help you get that perfect shot:
- Use a Tripod: Stability is key when shooting in low light conditions.
- Set the Right Exposure: A longer exposure (around 10-20 seconds) can help capture the vibrant colors of auroras.
- Choose a Wide-Angle Lens: This will allow you to capture more of the sky in your frame.
- Experiment with ISO Settings: Start with ISO 800-1600 and adjust based on the brightness of the auroras.
Remember, patience is your best friend when it comes to aurora photography. Sometimes it takes a while for the lights to fully develop, so be prepared to wait it out.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While photographing auroras might seem straightforward, there are a few pitfalls to watch out for:
- Overexposure: Too much light can wash out the colors of the auroras. Stick to shorter exposures if the lights are particularly bright.
- Shaky Camera: Even the slightest movement can ruin your shot, so make sure your tripod is sturdy and level.
- Ignoring Foreground Elements: Incorporating interesting landscapes or objects in the foreground can add depth and context to your photos.
Fun Facts About Red and Green Lights in the Sky
Here are some cool tidbits to impress your friends with:
- Auroras can sometimes produce sounds, though scientists aren’t entirely sure why. Some people describe it as a faint crackling or rustling noise.
- While the northern lights (Aurora Borealis) are the most famous, there’s also a southern counterpart called Aurora Australis.
- Earth isn’t the only planet with auroras. Jupiter and Saturn also experience stunning light shows, thanks to their strong magnetic fields.
Challenges in Studying Auroras
Despite our advances in technology, studying auroras still presents several challenges. For one, they’re highly unpredictable. Even with the best forecasting tools, scientists can’t always pinpoint exactly when and where auroras will occur. Additionally, the remoteness of aurora-prone regions makes research logistically difficult.
That said, modern tools like satellites and ground-based observatories are helping scientists gather more data than ever before. By combining observations from space and Earth, researchers are slowly unraveling the mysteries of these captivating lights.
Conclusion
So there you have it—a deep dive into the world of red and green lights in the sky. From their formation to their cultural significance, auroras are a testament to the beauty and complexity of our universe. Whether you’re a scientist, a photographer, or just someone who loves staring at the stars, these natural electrical phenomena are worth exploring.
Now it’s your turn! Have you ever seen an aurora in person? What was it like? Drop a comment below and let us know. And if you enjoyed this article, don’t forget to share it with your friends. Who knows? You might inspire someone to chase the northern lights themselves!
Table of Contents
- What Are Red and Green Lights in the Sky?
- How Do Auroras Form?
- Factors Influencing Aurora Activity
- Where Can You See Red and Green Lights in the Sky?
- Why Are Red and Green Lights in the Sky Important?
- Historical Significance of Auroras
- How to Photograph Red and Green Lights in the Sky
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Fun Facts About Red and Green Lights in the Sky
- Challenges in Studying Auroras


Detail Author:
- Name : Brooks Moen
- Username : norwood.borer
- Email : dallas.roob@grady.org
- Birthdate : 1998-04-23
- Address : 39804 Quigley Garden Ratkeshire, AR 44405-9346
- Phone : +1-567-899-6257
- Company : Wyman Group
- Job : Supervisor Correctional Officer
- Bio : Rem ut aperiam quia iste soluta alias. Et aut quos est est voluptate deleniti. Unde delectus quis cupiditate impedit aut odit.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/evelyn5189
- username : evelyn5189
- bio : Sequi rem eligendi temporibus sed a.
- followers : 4069
- following : 1663
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/wildermane
- username : wildermane
- bio : Quis odit eius accusamus. Dolorum architecto cum minima rem.
- followers : 799
- following : 983